T2I-ConBench: Text-to-Image Benchmark for Continual Post-training
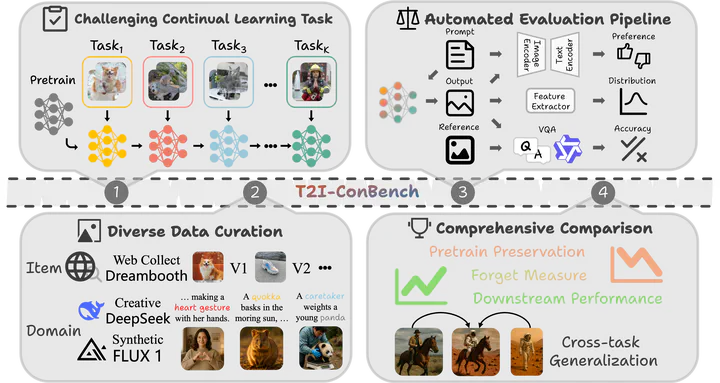 Overview of T2I-ConBench benchmark for continual post-training of text-to-image diffusion models
Overview of T2I-ConBench benchmark for continual post-training of text-to-image diffusion modelsOverview
This paper tackles continual post-training of large text-to-image diffusion models, where a single pretrained model must be sequentially adapted to new tasks while preserving its original capabilities and avoiding catastrophic forgetting.
To overcome the lack of a standard evaluation protocol, the authors propose T2I-ConBench, a unified benchmark for continual post-training that systematically measures how well methods retain general generative abilities, adapt to new tasks, prevent forgetting, and generalize across tasks.
Key Contributions
- Unified benchmark for continual post-training: Introduces T2I-ConBench as a comprehensive benchmark specifically designed for continual post-training of text-to-image diffusion models, rather than generic continual learning or one-shot fine-tuning.
- Two practical scenarios: item customization and domain enhancement: Covers personalized item customization and domain enhancement as two realistic and complementary post-training settings, reflecting common deployment needs for T2I models.
- Four evaluation dimensions: Evaluates methods along four axes: (1) retention of pretrained generality, (2) target-task performance, (3) catastrophic forgetting, and (4) cross-task generalization, enabling nuanced comparison of methods’ stability-plasticity trade-offs.
- Comprehensive automated evaluation pipeline: Combines standard image-text metrics, a learned human-preference model, and vision-language QA into an automated pipeline to approximate human judgment and assess both quality and alignment.
- Systematic benchmarking of methods: Benchmarks ten representative continual post-training methods on three realistic task sequences, revealing that no single method is best on all metrics, that oracle joint training is not always ideal, and that cross-task generalization remains unsolved.
- Open resources: Releases datasets, code, and evaluation tools to support future research and reproducible comparisons in continual post-training for text-to-image diffusion models.
Method
The T2I-ConBench framework formalizes continual post-training as sequential adaptation of a fixed, pretrained text-to-image diffusion model on a series of disjoint task datasets, without revisiting earlier data.
Core components include:
- Task sequences: Carefully designed continual task sequences that mix item customization and domain enhancement tasks, reflecting realistic streams of user demands and domain shifts.
- Curated datasets: Diverse item-level datasets for personalized concept learning and domain-specific datasets (e.g., synthetic or specialized domains) for enhancement of generation quality and alignment.
- Evaluation pipeline: An automated pipeline that:
- Uses standard T2I metrics for fidelity and alignment,
- Employs a human-preference model to approximate subjective judgments,
- Uses vision-language QA to test semantic consistency and compositional understanding.
- Assessment across four axes: For each method and task sequence, T2I-ConBench measures:
- Retention of generality – how well pretrained capabilities are preserved,
- Target-task performance – quality and alignment on the current task,
- Catastrophic forgetting – degradation on earlier tasks,
- Cross-task generalization – ability to compose concepts from multiple tasks in novel prompts.
By fixing the base model, tasks, and evaluation protocol, T2I-ConBench isolates the effect of the continual post-training algorithm itself, enabling fair and reproducible comparison across methods.
Citation
If you find this work useful for your research, please consider citing:
@article{huang2025t2iconbench,
title = {T2I-ConBench: Text-to-Image Benchmark for Continual Post-training},
author = {Huang, Zhehao and Liu, Yuhang and Lou, Yixin and He, Zhengbao and He, Mingzhen and Zhou, Wenxing and Li, Tao and Li, Kehan and Huang, Zeyi and Huang, Xiaolin},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.16875},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2505.16875}
}