A Unified Gradient-based Framework for Task-agnostic Continual Learning-Unlearning
May 21, 2025· ,,,,,,,·
2 min read
,,,,,,,·
2 min read
Zhehao Huang
Xinwen Cheng
Jie Zhang
Jinghao Zheng
Haoran Wang
Zhengbao He
Tao Li
Xiaolin Huang
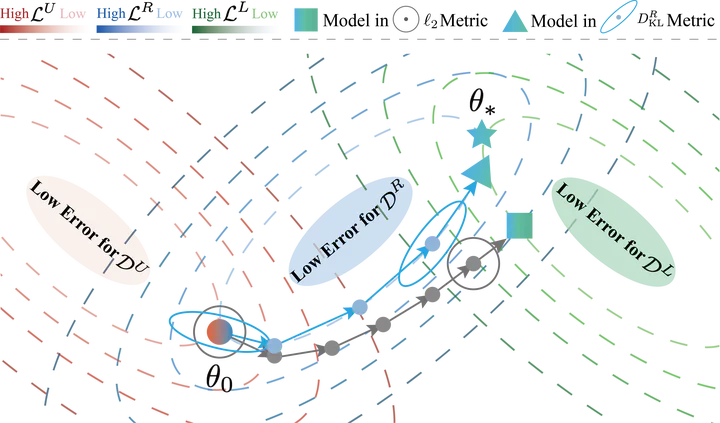 Unified gradient-based framework for task-agnostic continual learning-unlearning
Unified gradient-based framework for task-agnostic continual learning-unlearningAbstract
Recent progress in deep learning has created a need for intelligent systems that can both acquire new knowledge over time and reliably remove or revise previously learned information. This work introduces a unified gradient-based framework for task-agnostic continual learning-unlearning (CLU) that treats continual learning (CL) and machine unlearning (MU) as two sides of the same optimization problem. By formulating CLU as the minimization of a Kullback-Leibler divergence objective, the authors decompose gradient updates into four components corresponding to learning new knowledge, unlearning targeted data, preserving existing knowledge, and modulating updates via weight saliency. To address the stability-plasticity trade-off that arises during sequential learning-unlearning cycles, the framework incorporates a remain-preserved manifold constraint, which induces a Hessian-based correction term to better maintain performance on retained data. Building on this formulation, the paper proposes the UG-CLU algorithm, featuring a fast-slow weight adaptation scheme, adaptive weighting coefficients, and a balanced saliency mask for efficient second-order-aware optimization. Beyond conventional task-aware settings, the authors further define task-agnostic CLU scenarios that support fine-grained unlearning at both class and sample levels. Experiments on multiple benchmarks and architectures show that the proposed approach achieves a favorable balance between incremental learning accuracy, precise unlearning, and long-term knowledge stability.
Type
Publication
In arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.15178
Overview
This paper introduces a unified gradient-based framework for task-agnostic continual learning-unlearning (CLU), in which continual learning (CL) and machine unlearning (MU) are modeled within a single KL-divergence-based optimization view. By decomposing gradient updates into interpretable components and correcting them with a remain-preserved manifold, the framework aims to simultaneously enable efficient learning of new information, precise removal of targeted data, and preservation of existing knowledge.
Key Contributions
- Unified CL-MU Optimization Framework: Formulates CL and MU as a joint optimization problem based on Kullback-Leibler divergence minimization, revealing their intrinsic connection under a common gradient-based view.
- Decomposition of Gradient Updates: Shows that approximate CLU updates can be decomposed into four parts: learning new knowledge, unlearning specified data, preserving remaining knowledge, and modulating updates via weight saliency.
- Remain-preserved Manifold with Hessian Compensation: Introduces a manifold constraint that induces a Hessian-based correction term, improving the trade-off between stability on retained data and plasticity for new tasks.
- UG-CLU Algorithm: Proposes a practical implementation featuring a fast-slow weight adaptation mechanism, adaptive weighting coefficients, and a balanced weight saliency mask for efficient second-order-aware optimization.
- Task-agnostic CLU Scenarios: Extends beyond task-aware settings to support fine-grained, task-agnostic unlearning at both class and sample levels, aligning with realistic privacy and compliance requirements.
- Extensive Empirical Evaluation: Demonstrates that the framework effectively balances incremental learning performance, unlearning quality, and knowledge stability across multiple datasets and architectures.
Citation
If you find this work useful for your research, please consider citing:
@article{huang2025unified,
title = {A Unified Gradient-based Framework for Task-agnostic Continual Learning-Unlearning},
author = {Huang, Zhehao and Cheng, Xinwen and Zhang, Jie and Zheng, Jinghao and Wang, Haoran and He, Zhengbao and Li, Tao and Huang, Xiaolin},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.15178},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2505.15178}
}